What is the Trigonometric ratio for sine Z — Explanation & Interactive Diagram
What is the Trigonometric ratio for sine Z? In this section we explain the definition, show a live diagram you can interact with, provide examples, and answer common questions — all focused on the phrase What is the Trigonometric ratio for sine Z.
Definition — What is the Trigonometric ratio for sine Z?
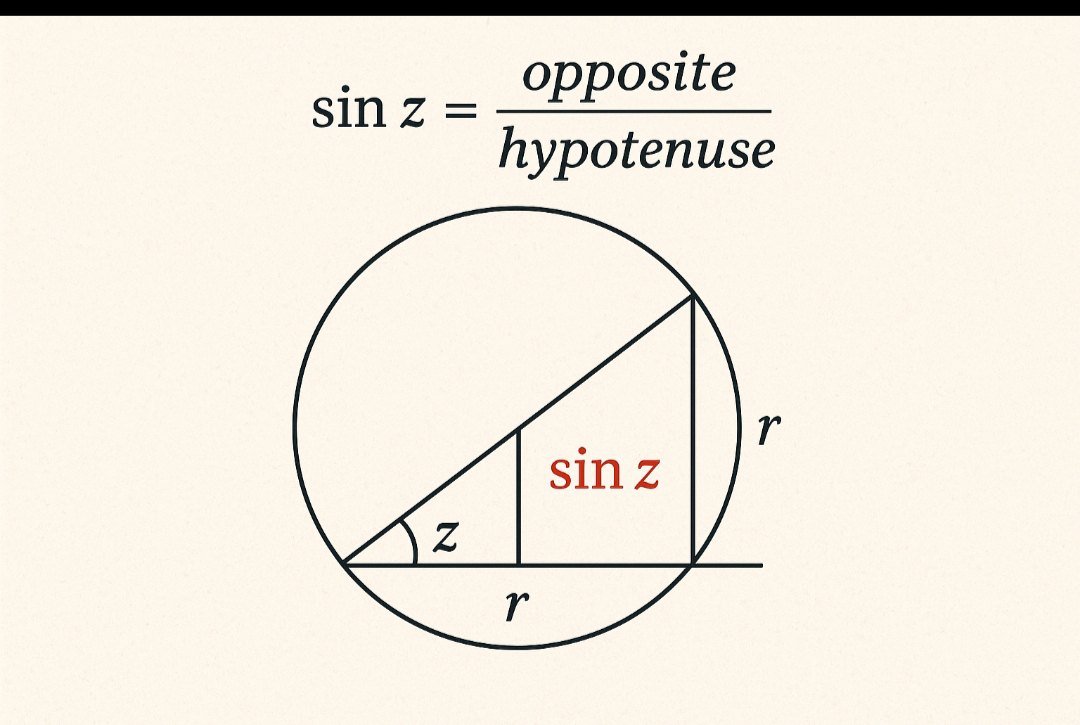
By definition, the trigonometric ratio for sine Z (written sin Z) is the ratio of the length of the side opposite angle Z to the hypotenuse in a right triangle:
sin Z = opposite / hypotenuse
On the unit circle (radius = 1), sin Z equals the y-coordinate of the point reached by rotating from the positive x-axis by angle Z (measured in degrees or radians).
Unit circle diagram (interactive)
Move the slider to change Z (angle) and watch the point move — the y-value displayed is sin Z, illustrating What is the Trigonometric ratio for sine Z.
cos Z (x) = 0.866
Description of diagram
This interactive shows the unit circle (radius = 1). The point on the circumference corresponds to angle Z. The vertical projection from the point to the x-axis gives the sin Z value (y-coordinate). Use the slider to change the angle and see how What is the Trigonometric ratio for sine Z varies.
Quick notes
- Range: −1 ≤ sin Z ≤ 1
- Period: sin(Z + 360°) = sin Z (or sin(z + 2π) = sin z)
- Angle units: degrees or radians
Properties & formulas (using the keyword)
Basic identities including “What is the Trigonometric ratio for sine Z”
sin²Z + cos²Z = 1sin(-Z) = -sin Zsin(90° − Z) = cos Zsin(A ± B) = sin A cos B ± cos A sin B
Worked examples — answering “What is the Trigonometric ratio for sine Z”
- Right triangle: If the opposite = 3 and hypotenuse = 5,
sin Z = 3/5 = 0.6. - Unit circle: Z = 30° →
sin 30° = 0.5. - Using identities: If
cos Z = 0.8and Z in first quadrant,sin Z = sqrt(1 - 0.8²) = 0.6.
Frequently asked questions — What is the Trigonometric ratio for sine Z (20)
1. What is the trigonometric ratio for sine Z in words?
2. How do I calculate sin Z from a right triangle?
3. What is sin 90° for Z = 90°?
4. Can sin Z be negative?
5. What units can Z be in?
6. What are common exact values of sin Z?
7. How does the unit circle show “What is the Trigonometric ratio for sine Z”?
8. Is sin Z periodic?
9. How to compute sin Z on a calculator?
10. What is the derivative of sin Z?
11. What is the integral of sin Z?
12. How to find angle Z if sin Z is known?
13. Can sin Z = 2?
14. Relationship between sin Z and cos Z?
15. What is sin(180° − Z)?
16. Common mistakes when using sin Z?
17. How to express sin Z in terms of complex exponentials?
18. How is sin Z used in real-world contexts?
19. Can you compute sin Z from coordinates?
20. Where else should I learn about sin Z?
Resources links
Internal page: Explore Detailed study of Trigonometry (internal)
Outbound resource: Khan Academy — Trigonometry